[ China Instrument Network Instrument Research and Development ] Recently, Luo Yunjiu of the School of Science and Technology at Jinan University has proposed an enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensor using a tungsten disulfide nano-film covering layer.
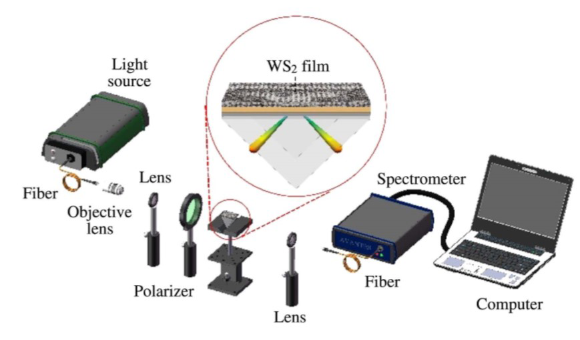
Experimental setup for refractive index sensing measurements
Tungsten disulfide (WS2) is a representative layered transition metal dihalo acid (TMDC) material, which has important application prospects in high-sensitivity sensors. Here, the researchers proposed a sensitivity-enhanced surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor with a metal film with an improved WS2 nanofilm coating. The SPR sensitivity is related to the thickness of the WS2 coating, which can be adjusted by coating different concentrations of the WS2 ethanol suspension or repeating the number of coating applications. Due to its large surface area, high refractive index and unique optoelectronic properties, the WS2 nanosheet coating layer coated on the gold film significantly improves the sensing sensitivity. By coating the WS2 suspension once, they achieved a higher sensitivity (up to 2459.3 nm/RIU) in the experiment. Compared with the absence of WS2 overlay, this result shows a 26.6% increase in sensitivity. The researchers analyzed and discussed the effect of WS2 nanofilm coating on the improvement of sensing performance. In addition, the linear correlation coefficient of the proposed WS2 SPR sensor in the refractive index range of 1.333 to 1.360 is 99.76%. In addition to the increased sensitivity, the WS2 nanosheet overlay can also exhibit additional advantages such as protecting the metal membrane from oxidation, tunability in the resonant wavelength region, biocompatibility, vapor capabilities, and gas sensitivity.
In recent years, due to the dual transition metal dihalide (TMDC), such as molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and tungsten disulfide (WS2), due to its unique electrical, optical, plasma, electrochemical and electrocatalytic properties The atomic thin layer structure has become more and more important among various disciplines. WS2 has a hexagonal crystal structure formed by covalently attached S-WS monolayers and is superposed by weak van der Waals forces. The WS2 monolayer contains a layer of tungsten atoms with sixfold coordination symmetry, which is symmetrically filled between the two triangular atoms of the sulfur atoms. Therefore, WS2, one of the newly emerging 2D layered nanomaterials, is considered to be a graphene-based material. There are many techniques for TMDC synthesis, such as chemical vapor deposition, mechanical spalling, and liquid phase stripping methods. As a typical TMDC material, WS2 has strong photoluminescence, large photoresponsivity, high density of electronic states, large bandgap in the visible to near-infrared spectrum, and high surface-to-volume and layer-related electrons. And optical properties make it a promising material. There are many opportunities for the development of new biological and chemical sensors and sensing applications. For example, it has been reported that plasma-assisted synthesis of WS2 films has high sensitivity to the presence of NH3, indicating the potential of two-dimensional WS2 films for electrochemical gas sensing applications. A novel nano-WS2 nanosensor for ultra-sensitive detection of small molecule-protein-receptor interactions has been reported in the literature with a sensitivity of up to 5.3 pmol/L. Wrapped in a tapered region of the Wiener fiber, WS2 nanofilms have been proposed for enhanced moisture sensing.
(Original Title: Researchers at Jinan University Using Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors with WSS Nanofilm Coverage)
Escalator Roller, Escalator Roller Design
Realever Enterprise Limited , https://www.cnelevator-parts.com